Why does your child seek a variety of stimulations during their normal day-to-day activities? Kids seek simulations usually as an attempt to satisfy and regulate the nervous system. This thing is very important for children with autism spectrum disorder.
However, it is very important to note that most sensory-seeking behaviors are harmless. Sometimes it can be self-injurious behavior or dangerous climbing or jumping. That is why parents should pay attention to limiting or modifying the self-stimulation behaviors of their kids.
1. Who is a sensory seeker?
If somebody has a strong need for sensory input and activity and seeks out experience that provides intense varied sensory situations is called the sensory seeker. This behavior often shows a child.
This disorder can represent sensory processing disorder(SPD), autism spectrum disorder( ASD), or action deficit hyperactive disorder (ADHD).
The sensory seekers always try to run, jump, spin, and engage in various vigorous activities. Those we can ask about are mostly purposeless.
They perform various types of odd movement patterns to seek various types of sensory patterns.
They always touch objects constantly and feel the textures of people. This means they always try to see tactile stimulation.
They are always prepared to stay in an enjoy noisy environment and they might make loud noises, so they seek out loud musical activities. Those loud noises very much disturb other normal people and your child can enjoy those situations very much.
Open this children’s Messi out strong flavors mails sometimes even inappropriate or non-food items.
Also, these children may speak the adrenaline Rush from activities that others might find scary or risky. So these risky behaviors can take place when hiking heights going in slippery places, doing other types of scary things
These various types of behavior scans regulate the sensitive system of these children and it also helps them to feel more balance and control. Understanding and supporting these types of sensors is very important for 18 kids. Parents ko kya ki bus must provide them with appropriate sensory activities and an environment that meets their needs specially.
Especially your need to take the guidance of an occupational therapist in providing these types of sensory activities in a balanced way.
Practical Life Problems for sensory Seekers in the classroom
In practical life, the teacher of your kid’s classroom can share that your child is always trying to do the below things.
They never try to stop talking and always try to get into the faces of others and continue speaking
Circle time is a very difficult time for these kids. They always try to spin and jump. They also bump into others and often run into walls when in gym activities.
- They always try to break crayons and art class is a very difficult time for them. They push down the crayons and are so hard when coloring.
- The kids always try to talk with outside boys
- The children have fallen behind in skills such as cutting up with peers in sports, writing letters, etc.
- He is a Messi eater, usually unaware of foods that are left on the hands’ parts of clothing.
- If your kids have these types of complaints from their teachers in the classrooms you better get 10 professional assistants such as occupational therapy assistants or any other medical personal assistant to assess the sensory levels of your kid

2. Signs of sensory-seeking kids
- The kids constantly touch people know objects around them
- It is very difficult for them to sit still in one place
- Constantly been on the go
- They always take risks at playgrounds or play areas
- They frequently try to pick at their fingers
- They always try to fall on something without regarding the safety
- They always try to see the smell of food and food items while mouthing Nonfood items
- They always watch as others move around the room or the play area o type of a crowded place.
Other Symptoms of sensory-seeking behaviors
The manifestation of the sensory is rich in behavior very different. It depends on which type of sensory input the kids are craving.
The tactile-sensitive seeking
- They frequently touch people or objects even when it is inappropriate.
- They always prefer mud, paint, and sand and enjoy Messi playing with them
- One of the main things is they always couch different textures by robin the hand so other body parts are against the surfaces. These surfaces can be a wall a toy a playmate or any other dressing material that day frequently wears.
- Most of the oral sensory problems are sensory seeking so they often eat non-food items in their mouth.
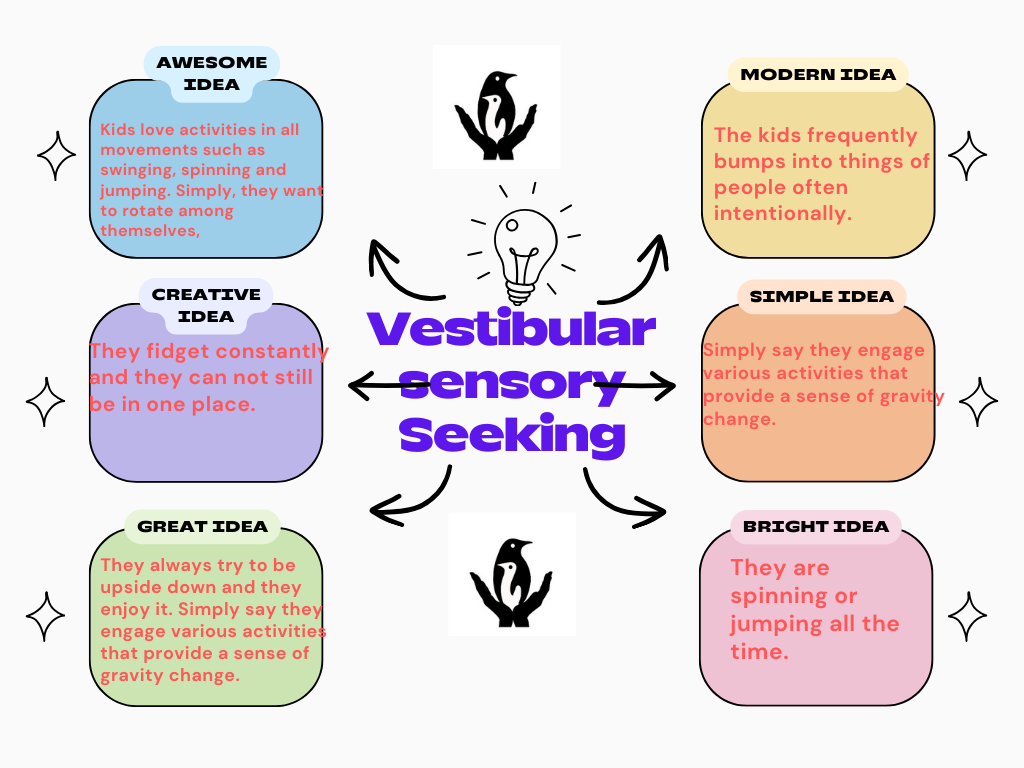
Types of vestibular sensory seeking
- Kids love activities in all movements such as swinging, spinning, and jumping. Simply, they want to rotate among themselves, that’s why they are spinning or jumping all the time.
- They fidget constantly and they can not still be in one place.
- They always try to be upside down and they enjoy it. Simply put they engage in various activities that provide a sense of gravity change.
A few types of body awareness sensory seeking and that is called proprioceptive sensory seeking
- The kids frequently bump into things of people often intentionally. They get a sensory shooting effect by doing this type of activity
- always hugging,deep-pressure activities of roughhousing.
- try to choose clothing, pencils other objects in the class in the house
- Scratch into the walls, cushions, and other surfaces
The auditory sensory seekings
- The kids like to make very loud noises all the time such as banging objects and shouting
- always try to spin objects of patterns and they are fascinated by doing those
- engage in various types of video games for extended periods or watch similar videos for screen activities.
Smell and taste sensory-seeking behaviors
- These kids always try to snip off people frequently
- Attached to very strong smells disregarding that they are pleasant or unpleasant
- They always ask for spicy foods or strong-tasting food items
- The kids often chew nonfood items that can be toys classroom materials or any other home material
In general, the sensory-seeking behavior that kids appear is always hyperactive or overly energetic. They have difficulty translating into various types of activities so they need little assistance to initiate a neighboring introduced activity type.
-Defineed sensory seeking behavior-
These kids always try to do risky behaviors and they may be impulsive all the time. Their attention and focus are very minimal within a less stimulating environment.
3. What has happened? The science behind sensory-seeking behavior.
The human brain has a proper way of processing the sensory information. The sensory-seeking behavior is rooted in that.
How the brain understands the sensory processing
Our nervous system receives messages from the senses and eventually turns them into appropriate motor and behavioral responses. This procedure is called sensory processing.
Firstly the sensory receptors in the sensory organs such as eyes, ears, skin, etc. detect the stimuli. After these receptors send signals to the brain via the nervous system. Our brain can interpret these signals and understand what they mean.
Finally, the relevant body parts react to the brain signals with movements and actions.
Sensory seeking: A type of sensory processing difference
Sensory-seeking kids have a high threshold of sensory input. It means they have a sensory processing difference. They need more intense or varied sensory experiences to achieve their optimal arousal.
So the sensory seekers have high sensory thresholds. Their brains do not normally register the sensory inputs easily like others. They may have a difference in the sensory pathways. So the brain’s sensory integration centers do not function as normal people.
Sensory-seeking behaviors can link with the brain’s dopamine system, which is a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. These sensory-seekers have a baseline level of altered dopamine receptor function.
The brain has mechanisms to maintain an optimal level of arousal. For sensory seekers, typical sensory input may not be sufficient to maintain this balance, leading them to seek additional stimuli to reach a comfortable state of arousal.
4. Types of Sensory Input
- Tactile (Touch): Tactile seekers might crave intense or varied tactile experiences. They have under-responsive tactile receptors that require stronger stimuli to send signals to the brain.
- Vestibular (Movement): The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, helps control balance and spatial orientation. The vestibular seekers may need more movement to stimulate this system adequately.
- Proprioceptive (Body Awareness): Proprioception involves sensing the position and movement of the body. Proprioceptive seekers might engage in activities that provide deep pressure or heavy work to stimulate proprioceptive receptors.
- Auditory (Hearing): Auditory-seekers loud or complex auditory stimuli to meet their sensory needs, possibly due to under-responsive auditory pathways.
- Visual (Sight): Visual sensory seekers might be drawn to bright lights, patterns, or fast-moving visuals to adequately stimulate their visual area of the brain.
- Olfactory (Smell) and Gustatory (Taste): Seeking strong smells or tastes can be a way to stimulate the olfactory and gustatory systems, respectively.
5. The list of Common sensory-seeking behaviors.
Constantly been on the go
The kids constantly touch people know objects around them
It is very difficult for them to sit still in one place
They frequently try to pick at their fingers
They always take risks at playgrounds or play areas
They always try to fall on something without regarding the safety
They always try to see the smell of food on and food items while mouthing food items
They always watch as others move around the room or the play area or type of crowded place.
6. How does sensory seeking impact the daily life of your kid?
A sensory-seeking child has to face a lot of challenges in his daily life. It can vary into several areas of the activities of daily living their lives. First, it is important to consider the challenges in the classroom activities.
They may have a lot of concentration issues in the classroom. If a certain activity does not meet his sensory requirement, they can not concentrate on doing that properly. Eventually, they lead to difficulties in completing classroom tasks.
If a child is unable to fulfill several sensory needs such as the need to move around, touch objects, or make noises, then that need turns into behavioral impact for them. Finally, that can lead to misunderstandings with teachers and colleagues.
A healthy child needs to develop a lot of social interactions with others. However, a few of their sensory-seeking behaviors are misunderstood by their peers in daily social life. That can lead to social isolation or difficulties in forming new relationships.
Some sensory-seeking behaviors lead to the development of play preferences of your kid. Sometimes these sensory kids may prefer the most active and physically engaging play. That engagement can be overwhelming to others. Also, these kids have problems in dressing and grooming and with various eating habits.
Sensory-seeking kids have problems adhering to typical household activities and it’s routines. It may be sitting quietly at the dinner table or going to bed at the regular time. So their daily lifestyle becomes a more disruptive task for them. so the parents need to provide them with relevant sensory breaks or activities to help them self-regulate and maintain a calm state.
These kids are easily frustrated while doing their daily activities. Dear parents, you need to understand the emotional regulation part of your kid. So try to understand and provide them with the relevant sensory part at relevant times. Meantime try to learn and practice good coping mechanisms with your kid.
Sensory-seeking kids have various creative ways to fulfill their sensory needs. That ability can foster their innovative thinking patterns and problem-solving skills.
7. Strategies for supporting your sensory-seeking kid
Parents can provide varied sensory activities for the kids. They can make many sensory bins with their creative ideas by filling those with rice, sand, or beans for various tactile exploration. Also can use various colored liquids to get visual sensory stimulation by making sensory bottles.
Using sensory toys with different textures, sounds, and visual stimuli can provide your kid lot of sensory inputs. These are among the chewable jewelry, fidget spinners, stress balls, etc.
Parents can make a Friendly environment for their sensory-seeking kids. You can adjust the lighting and sounds of your home. Try to use dim lighting, usage of noise-canceling headphones, or soft background music to create a soft atmosphere around the home.
Dear parents, you can talk to your Occupational therapist or relevant medical person to create and maintain a predictable daily routine for your kid. That will your child to reduce their anxiety and have a secure feeling.
Sometimes most parents may not be willing to do heavy work activities with their little kids. But it can regulate their energy levels. So parents can engage the child in carrying heavy objects such like carrying groceries, pushing a vacuum, or pulling resistance bands, etc. These pushing, pulling, and lifting activities are very good for them.
Nowadays, a lot of sensory tools and equipment are available on the market. Parents can use weighted vests or blankets for kids. it can provide a deep pressure effect that will calm and organize the nervous system. Also, kids prefer therapy balls to do exercises for the core muscles of the body and that gives them correct sensory input.
Parents can work with their Occupational therapists and provide tailored sensory diets for the kids. This personalized plan of sensory activities is designed to meet the child’s specific needs. Maintaining regular intervals with the sensory diet activities is very important.
A parent should be a good educator for their kid. They can teach various self-regulation techniques to the kids. Deep breathing techniques with mindfulness and relaxation exercises are very important. Yoga is very effective in doing this.
Finally, parents should give positive reinforcement to encourage positive behaviors. you can build up a child’s confidence level by celebrating their success and progress.
8. Few occasions that you need to limit sensory seeking

First of all, parents need to think about whether the seeking behavior is potentially dangerous or not. If you notice that the sensory-seeking behavior is dangerous, then you need to reduce that behavior pattern for safety reasons. Parents need to identify these sets of children. Those children may engage in hitting themselves, head banging, biting, or digging themselves.
Some children are seeking out frequent slamming, head banging, hitting, and self-biting. These types of behaviors are often to be interrupted. If the parents fail to interrupt those behaviors, that particular behavior type will become intense and more frequent. Eventually, the children get addicted to that particular behavior.
Then they try to repeat certain movement patterns for self-calming and soothing. The self-calming and self-soothing behavior mechanisms are very important to soothe their nervous system.
You need to understand the inside physiological mechanism of intense stimulation. These intense stimulations can release endorphins in the nervous system. Eventually, the child will become normal because their system is never saturated with sensory stimulations with the help of that intense stimulation.
The problem is the child can become addicted to that intense stimulation. Finally, kids seek intense stimulation at a high cost. When this procedure is going on the brain, which tends to habituate, becomes numb to stimulation that occurs regularly.
The habituation of strong brain stimulation is not a good thing. Children will have to do it strongly to activate the release of endorphin levels in their brains.
We can explain this by an example. If your child digs at his skin to create stimulation to wake up his body, that simple stimulation can release endorphins inside the brain. This little amount of endorphins feels good and can control the body.
But the problem is, they are becoming addicted to that small level of endorphin. And the next time they need a high volume of endorphins feels so good. So the child starts to frequently dig off his surface skin and the skin will eventually create scar tissue which will have less feeling.
Children will have to dig deep with more intensity to elicit the same sensation at another time.
But this behavior is not practical. Because it will habituate their brain and they eventually become more tolerant of the simulations. And they unanimously raise the threshold for feeling the familiar stimulation towards their body.
When scar tissue forms at the surface of the skin, it will also dull the sensation. So now you can understand that your child is in danger of obtaining sensory stimulation to make his body calm.
So this type of self-harm, self-injured behavior needs to be modified, so then it is no longer injurious. But here we are not suggesting that the particular behavior should not necessarily be eliminated. we suggest only modifying the behavior.
9. Modulating the sensory stimulation
However, the problem is that the sensory seekers have trouble modulating the simulations. It means they don’t know how much they are nervous system exactly needs to make them soothe.
So these innocent kids are trying to seek a particular sensory-seeking behavior to its extreme levels. Finally, the kids often become dysregulated. Children don’t have a volume control that lets them know what is just right.
In those instances, parents need to regulate the simulation’s intensity and frequency to organize the child. It means pacing the child.
Eventually, the child provides his nervous system with organizing stimulation without overwhelming it.
10. Become fixating on sensory seeking
If the sensory-seeking behavior interferes with engaging in functional learning opportunities, your child may become fixated on sensory-seeking.
During this fixated situation, the sensory seeking interrupts and interferes with the participation in daily activities of your kid. For these children, the parents or teachers should usually identify the times of the day which means the sensory breaks when the child can engage their sensory seeking and then build other forms of substitute stimulations.
The substitute stimulations are such as gum chewing, and fidgeting items to provide relevant tactile and proprioceptive stimulations
In this way, the parents can substitute more appropriate stimulations to promote organizing and allow the preferred sensory stimulation for the child in free time sessions to re-energize.
11. If the sensory-seeking is interrupting others
we earlier discussed that these types of sensory-seeking behaviors interfere with the child’s participation in functional learning opportunities.
Apart from that, it also interferes with the activity of others. If a child’s sensory-seeking behaviors are interacting or significantly distracting to everyone around him then the parents need to look at it by substituting more acceptable stimulations and giving the child sensory breaks.
In the case of vocal steaming sensory-seeking behaviors are very much distracting to everyone around your child. So there is a time and place for everything. so think about that as parents and caregivers around the child.
Some other categories of children are engaged in sensory-seeking behaviors because it feels good to them. This type of seeking behavior does not necessarily help your children to connect a regulation or arousal level but occurs because it feels good to them. During this type of occasion, most children don’t have volume control and find it hard to turn it off once it is turned on.

If your child is engaging in the feel-good stimulations in extreme excess because it is good for them. lately, the baby become fixated on it. But the problem is they have poor volume control switches. With sensory addiction, these children also have trouble stopping a feel-good behavior once it gets going. This set of categories needs to set limits.
12. How to modify inappropriate sensory-seeking.
Parents can set limits by defining when, via, and for how long the child can engage in the stimulation. The parents may also have to define how intense the seeking can be.
It means, If the child doesn’t get this regulated by the sensory-seeking parents think about the intense levels of seeking behaviors.
As an example, we can provide child-specific times during the day at school to go to the resource promo another private area to engage in limited sensory-seeking behaviors
Parents can provide more appropriate substitutes for sensory-seeking behavior such as gum chewy tubing, fidgeting toys, and air cushions to sit, during the times when the prepared sensory seeking is not allowed to the child.
These substitutes for sensory stimulation can be tile auditory or proprioceptive stimulations. In doing so the parents can substitute one more acceptable, stimulation for another inappropriate stimulation.
If the child can perform at a good functional level with the substitute sensory-providing methods, then the parents can identify a more acceptable substitute that provides the same function.
As an example, provide substitute gum chewing for chewing on their clothes or fidget toys to provide tactile and proprioceptive stimulation to keep the child from picking at his skin. Also, you can provide music via an MP3 player to reduce vocal stimming.
Parents can provide a sensory diet that pins a mixture of various types of sensors if the child is doing the behavior to alert himself when aroused.
Sometimes children are trying to block out the provided stimulation to prevent overwhelming him. Then the parents need to modify the environment to get less noisy.
13. When to seek professional help?
Parents need to seek professional help when their sensory -seeking kid’s behavior intefere with daily fuctioning,pose safety risks,impact social interactions,hinder educational prograss or other significan behavioral challenges.
Early intervention and support can make significant difference. Then sensory-seeking kids manage their sensory needs effectively and improve thier quality of life.
First the parents should cosult a paediatrition and get the initial evaluation. After they can give modified sensory integration therapy. They can develop sensory diet activities.
If your child has significant behavirol and emtional issues, the psychologist or the psychiatrist can offer aditionnal assistance for you.
Dear parents, you can have a individualized education plan for your kid through your special education services. Also you can get the assistance of the parent supportive groups or commiunity groups for aditional assistance.
14. Conclusion.
Dear parents, you need to understand your sensory-seeking kid. They need your support a lot to adjust to the environment. Your patience, empathy, and proactive approach are very important for the child’s well-being. These children uniquely experience the world, craving sensory input that helps them feel balanced and secure
It is very important to recognize their needs and provide appropriate sensory activities. Parents should understand that every child is different and what works for one is not suitable for the other. So it is essential to identify the sensory needs well.
Parents should have skills such as following consistent routines and open communication is better to obtain good results. Also, parents should have a willingness to explore various sensory activities.
Finally, sensory-seeking children can channel their energy and develop thier skills which they need to succeed. Let’s celebrate their strengths and work together to create an environment where they can flourish. That is our ultimate joy as parents.